Have you ever ever ever wanted to transcribe one factor? Probably someone left a message in your voicemail, and likewise you wanted to put in writing it down on paper. Or probably you took notes in school, then rewrote them neatly that may help you analysis.
As these examples current, transcription is a course of throughout which knowledge is rewritten. Transcription is one factor we do in our regularly lives, and it’s also one factor our cells ought to do, in a additional specialised and narrowly outlined method. In biology, transcription is the tactic of copying out the DNA sequence of a gene in the identical alphabet of RNA.
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, throughout which knowledge from a gene is used to assemble a helpful product similar to a protein. The target of transcription is to make a RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence. For a protein-coding gene, the RNA copy, or transcript, carries the info wished to assemble a polypeptide (protein or protein subunit). Eukaryotic transcripts should endure some processing steps sooner than translation into proteins.
Contents
- 1 Transcription
- 2 Translation
- 3 Picture of Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet
- 4 Obtain Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet
- 5 The Genetic code
- 6 Some pictures about 'Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet'
- 6.1 dna transcription and translation worksheet
- 6.2 dna transcription and translation worksheet answer key
- 6.3 dna transcription and translation worksheet pdf
- 6.4 dna transcription and translation worksheet answers
- 6.5 dna transcription and translation worksheet answers pdf
- 6.6 dna transcription and translation worksheet svhs lab biology
- 6.7 dna transcription and translation worksheet key
- 6.8 dna transcription and translation worksheet svhs lab biology answers
- 6.9 dna transcription and translation practice worksheet answers
- 6.10 dna replication transcription and translation worksheet
- 7 Related posts of "Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet"
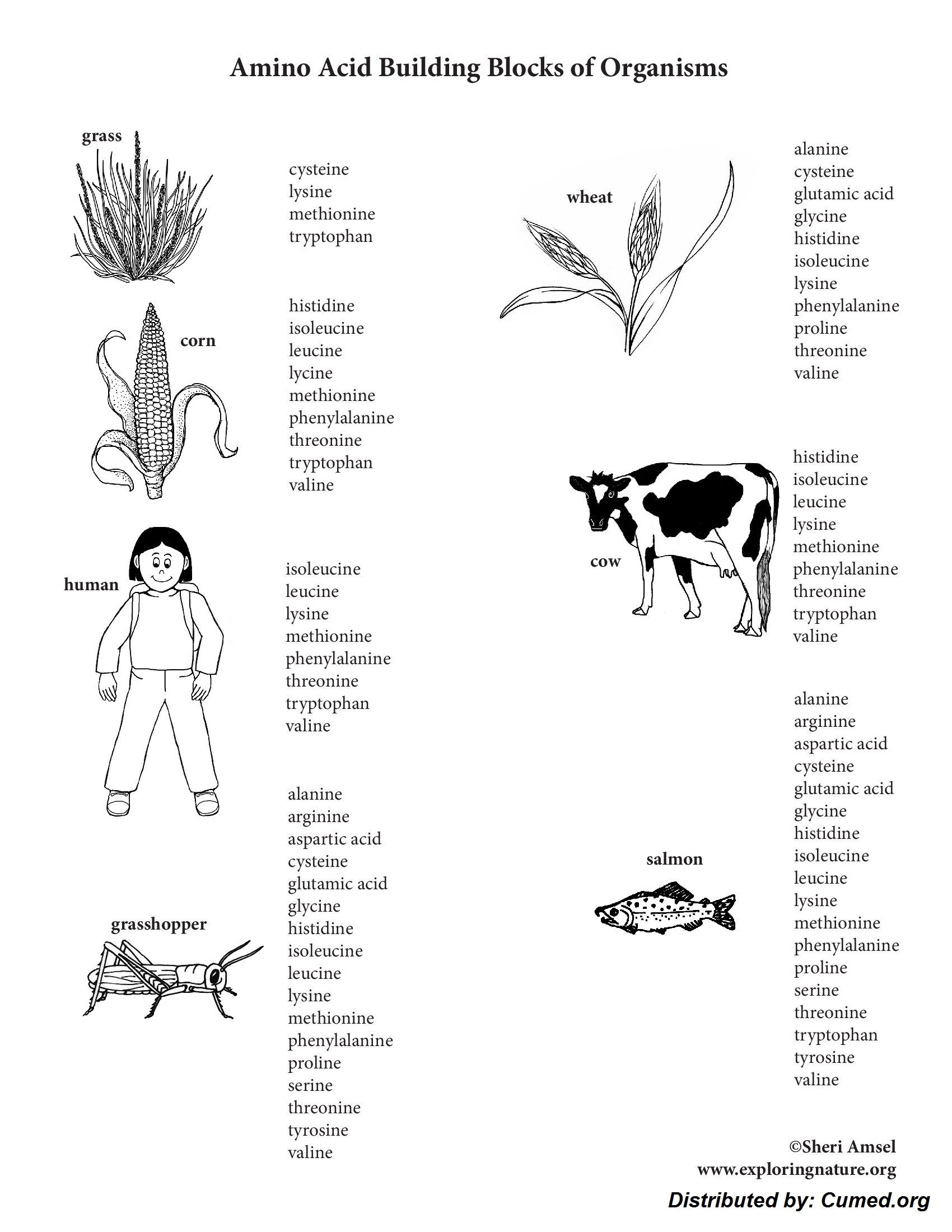
The genetic supplies is saved inside the kind of DNA in most organisms. In individuals, the nucleus of each cell contains three × 109 base pairs of DNA distributed over 23 pairs of chromosomes, and each cell has two copies of the genetic supplies. That’s recognized collectively as a result of the human genome. The human genome contains spherical 30 000 genes, each of which codes for one protein.
Large stretches of DNA inside the human genome are transcribed nevertheless do not code for proteins. These areas are generally known as introns and make up spherical 95% of the genome. The nucleotide sequence of the human genome is now recognized to an affordable diploma of accuracy nevertheless we do not however understand why a number of it is non-coding. Just a few of this non-coding DNA controls gene expression nevertheless the purpose of a number of it is not however understood. It’s a fascinating subject that is certain to advance shortly over the next few years.
Transcription
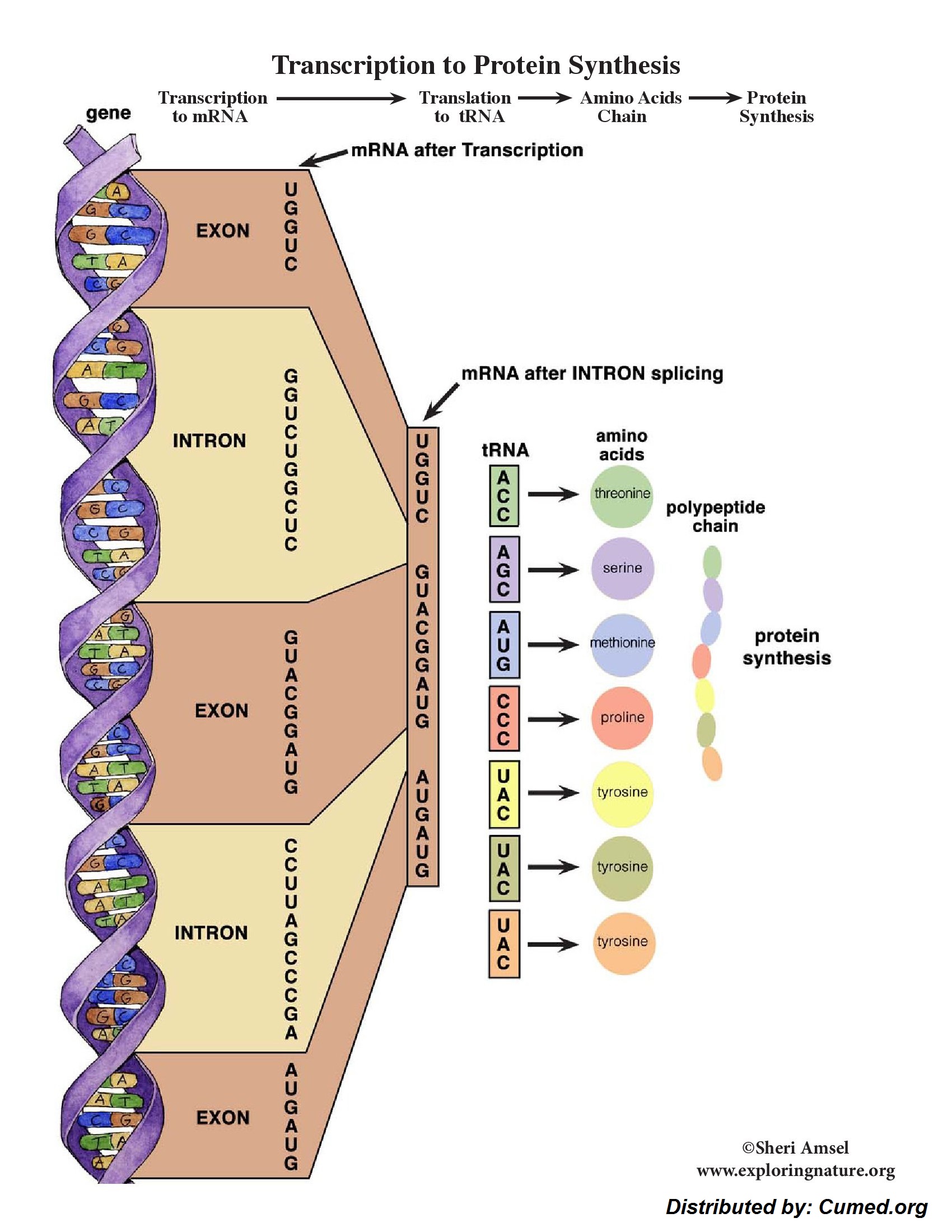
Transcription is the tactic by which DNA is copied (transcribed) to mRNA, which carries the info wished for protein synthesis. Transcription takes place in two broad steps. First, pre-messenger RNA is long-established, with the involvement of RNA polymerase enzymes. The strategy will depend on Watson-Crick base pairing, and the resultant single strand of RNA is the reverse-complement of the distinctive DNA sequence. The pre-messenger RNA is then “edited” to produce the desired mRNA molecule in a course of generally known as RNA splicing.
Formation of pre-messenger RNA
The mechanism of transcription has parallels in that of DNA replication. As with DNA replication, partial unwinding of the double helix ought to occur sooner than transcription can occur, and it is the RNA polymerase enzymes that catalyze this course of.
Not like DNA replication, throughout which every strands are copied, only one strand is transcribed. The strand that contains the gene is known as the sense strand, whereas the complementary strand is the antisense strand. The mRNA produced in transcription is a reproduction of the sense strand, nevertheless it is the antisense strand that is transcribed.
Ribonucleoside triphosphates (NTPs) align alongside the antisense DNA strand, with Watson-Crick base pairing (A pairs with U). RNA polymerase joins the ribonucleotides collectively to kind a pre-messenger RNA molecule that is complementary to a space of the antisense DNA strand.wxh Transcription ends when the RNA polymerase enzyme reaches a triplet of bases that is be taught as a “stop” signal. The DNA molecule re-winds to re-form the double helix.
Translation
The mRNA long-established in transcription is transported out of the nucleus, into the cytoplasm, to the ribosome (the cell’s protein synthesis manufacturing facility). Proper right here, it directs protein synthesis. Messenger RNA simply is not instantly involved in protein synthesis – swap RNA (tRNA) is required for this. The strategy by which mRNA directs protein synthesis with the assistance of tRNA is known as translation.
The ribosome is a extremely large sophisticated of RNA and protein molecules. Each three-base stretch of mRNA (triplet) is known as a codon, and one codon contains the info for a specific amino acid. As a result of the mRNA passes by the use of the ribosome, each codon interacts with the anticodon of a specific swap RNA (tRNA) molecule by Watson-Crick base pairing. This tRNA molecule carries an amino acid at its three’-terminus, which is built-in into the rising protein chain. The tRNA is then expelled from the ribosome. Decide 7 reveals the steps involved in protein synthesis.
Picture of Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet


Obtain Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet
Obtain Dna Transcription And Translation Worksheet: Click Here
The Genetic code
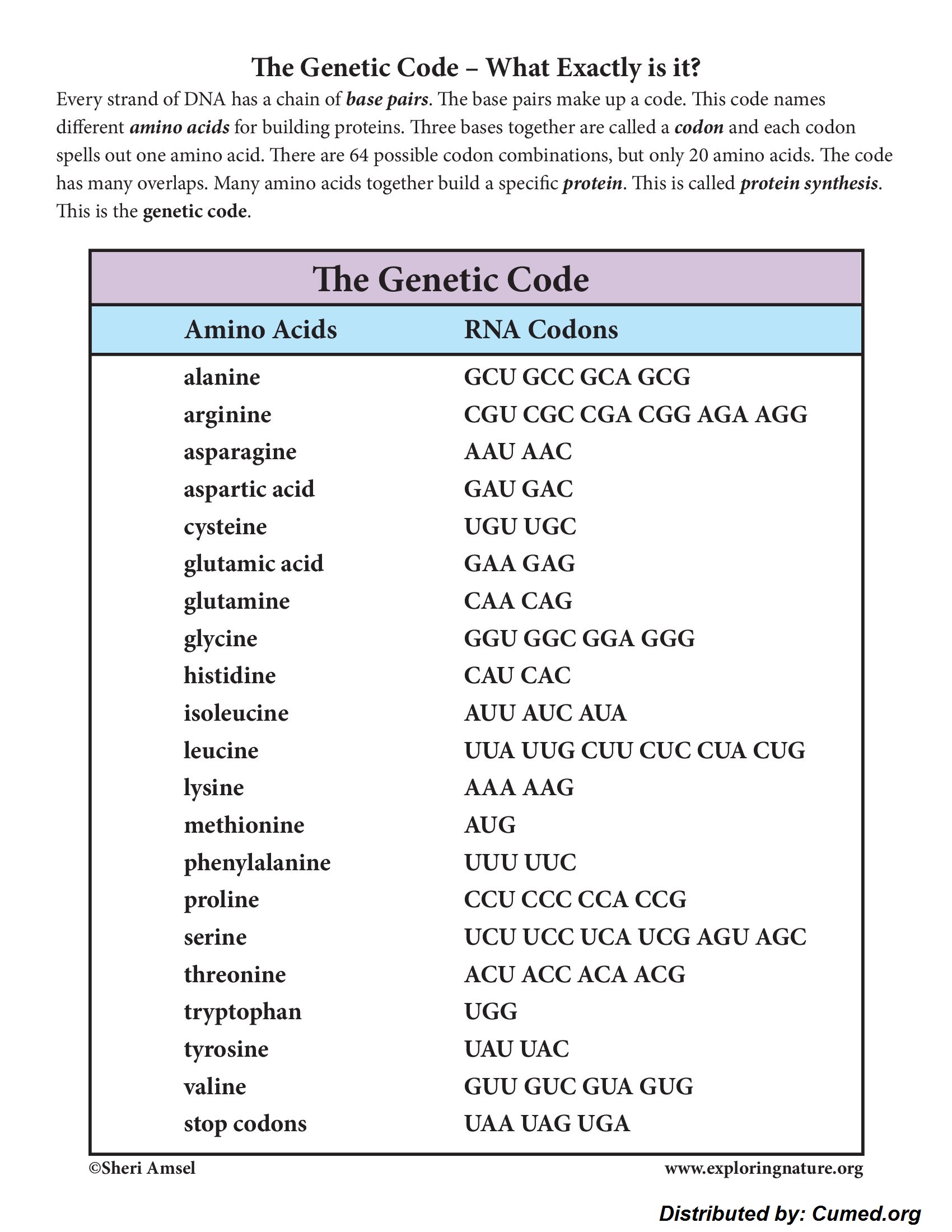
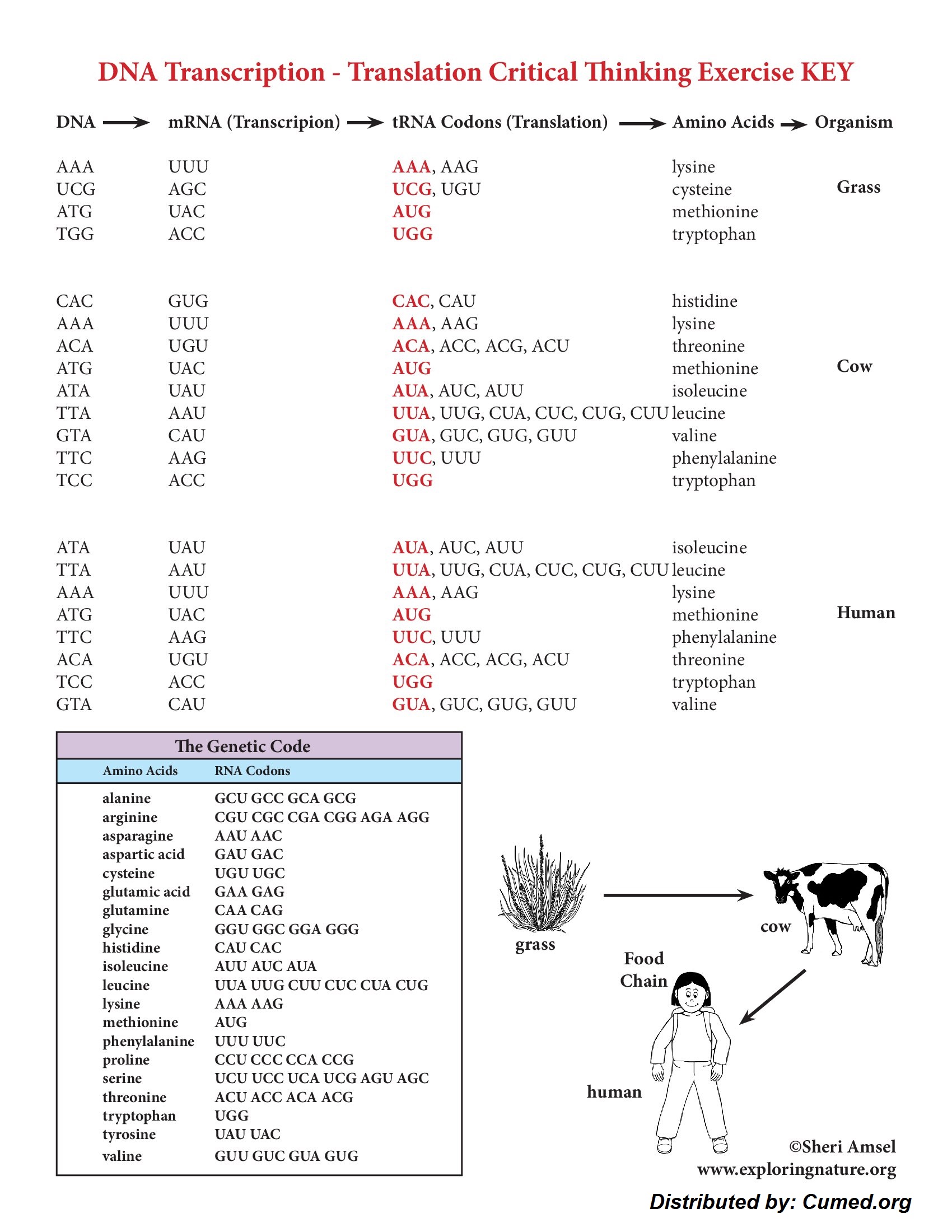
The genetic code is type of frequent. It is the inspiration of the transmission of hereditary knowledge by nucleic acids in all organisms. There are four bases in RNA (A,G,C and U), so there are 64 attainable triplet codes (4three = 64). In idea solely 22 codes are required: one for each of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids, with the addition of a start codon and a stop codon (to level the beginning and end of a protein sequence). Many amino acids have a variety of codes (degeneracy), so that all 64 attainable triplet codes are used. For example Arg and Ser each have 6 codons whereas Trp and Met have only one. No two amino acids have the an identical code nevertheless amino acids whose side-chains have associated bodily or chemical properties are prone to have associated codon sequences, e.g. the side-chains of Phe, Leu, Ile, Val are all hydrophobic, and Asp and Glu are every carboxylic acids (see genetic code). Which implies if the flawed tRNA is chosen all through translation (owing to mispairing of a single base on the codon-anticodon interface) the misincorporated amino acid will almost definitely have associated properties to the meant tRNA molecule. Although the resultant protein might have one incorrect amino acid it stands a extreme probability of being helpful. Organisms current “codon bias” and use certain codons for a particular amino acid higher than others. For example, the codon utilization in individuals is totally totally different from that in micro organism; it should in all probability usually be troublesome to particular a human protein in micro organism because of the associated tRNA may very well be present at too low a spotlight.
