While distance and displacement appear to have the same meaning, they actually have very different definitions and implications. Displacement is the measurement of “how far an object is out of place,” whereas distance refers to “how much ground an object has covered during its motion.” Let’s examine the distinction between distance and displacement in this post.
What is Distance?
Distance is the sum of an object’s movements, regardless of direction. Distance can be defined as the amount of space an object has covered, regardless of its starting or ending position.
What does “displacement” mean?
The term “displacement” refers to a shift in an object’s position. It is a vector quantity with a magnitude and direction. The symbol for it is an arrow pointing from the initial location to the ending place. For instance, if an object shifts from location A to position B, its position changes. Displacement is the term used to describe this shift in an object’s position.
Contents
- 1 What is Distance?
- 2 What does “displacement” mean?
- 3 Displacement and Distance Similarities
- 4 physical separations
- 5 Images of Distance And Displacement Worksheet
- 6 Download Distance And Displacement Worksheet
- 7 Conceptual Distances
- 8 Some pictures about 'Distance And Displacement Worksheet'
- 8.1 distance and displacement worksheet
- 8.2 distance and displacement worksheet grade 7
- 8.3 distance and displacement worksheet pdf
- 8.4 distance and displacement worksheet grade 7 pdf
- 8.5 distance and displacement worksheet with answers grade 7
- 8.6 distance and displacement worksheet with answers pdf grade 7 answer key
- 8.7 distance and displacement worksheet grade 5
- 8.8 distance and displacement worksheet grade 10
- 8.9 distance and displacement worksheet quizlet
- 8.10 distance and displacement worksheet grade 9
- 9 Related posts of "Distance And Displacement Worksheet"
Distance and displacement are two key words in mechanics that, despite having similar sounds, have distinct definitions and meanings. How much of an object’s path is covered by a moving object is measured in terms of distance. While “How much path is covered by the object in a specific direction” is measured by displacement, The main distinction between distance and displacement is therefore that the former is a scalar quantity while the latter is a vector quantity.
Both quantities have several commonalities despite this distinction. Meters are used to measure both length and displacement (m). In this article, we’ll learn more about distance and displacement by comprehending some key ideas, such as what distance is, its formula, what displacement is, its formula, its differences, similarities, and examples.
Regardless of the direction of the path, distance is the overall path that an object in motion has traveled. Since only the length of the path travelled is calculated and the direction of motion is ignored, distance is referred to as a scalar number. The distance can only ever be positive; it can never be 0 or negative.
Distance provides comprehensive knowledge about the full motion’s route. Since there is no need to indicate direction, distance is denoted by the letter “d” instead of an arrow.
Displacement is defined as the overall alteration of an object’s location and motion direction. Displacement is recognized as a vector quantity since it takes into account both the direction of the motion and the magnitude of the changing position. Displacement may be zero, positive, or negative.
The initial and final positions are needed in order to calculate displacement because displacement does not provide comprehensive information on the full path length. The letter “S” is used to symbolize displacement, and an arrow is used to show that it is a vector quantity. The path of displacement is always a straight line because the displacement is determined by connecting the start and end points.
Displacement and Distance Similarities
Both distance and displacement share many parallels despite their distinctions, some of which are described below:
- Only the meter (m) serves as the physical quantity’s SI unit.
- Initial and final points are needed to quantify distance and displacement, respectively.
- Most of the time, both magnitudes are equal when the direction is ignored.
- Both use the same formula for dimensions.
Displacement vs. Distance are two closely related terms that require exact definitions and comparisons. Displacement is the shortest distance between an origin and a particular destination, whereas distance is the actual path traveled.
An amateur may think that the terms “distance” and “displacement” sound quite familiar and comparable, but a physics teacher or student will understand these terms’ meanings much more clearly. For them, displacement and distance will be two separate words from the English language, yet these phrases will define a completely new physics idea. Even though they are estimated separately and may appear to someone to be very similar, distance and displacement actually have very different quantities and are relevant to one another.
We’ll present distance and displacement separately before moving on to the topic of distance vs. displacement.
Displacement vs. distance should be accurately contrasted using each term’s definition on its own. Distance is a measure of how far away two objects or locations are from one another. In physics or daily life, the term “distance” might refer to a physical distance or an estimate based on other criteria (for example, “two counties over”).
Distance is a non-numerical quantity in the social sciences and psychology; psychological distance is defined as “the various ways in which an object could be eliminated from” the self along dimensions like “social distance, time, space, and hypotheticality.”
The idea of distance can be better described with the help of an example. For instance, suppose you leave your office and walk five meters north, turn right again, walk five meters, turn right again, walk five meters, and turn right again, all while walking five meters. Although you will eventually arrive at the same location, the distance you have traveled is only 20 meters.
physical separations
Physical separation can convey a variety of ideas:
- Range of travel: the distance traveled on a specific route, such as while navigating a maze, between two places.
- Distance in a straight line: The distance along the shortest possible path between any two points in space, assuming no obstacles.
- geodetic separation The great-circle distance along the curvature of the Earth is an example of the shortest path length between two points while prevailing on a surface.
If a ball is thrown straight up or the Earth completes an orbit, the length of that path returns to the origin point.
Images of Distance And Displacement Worksheet


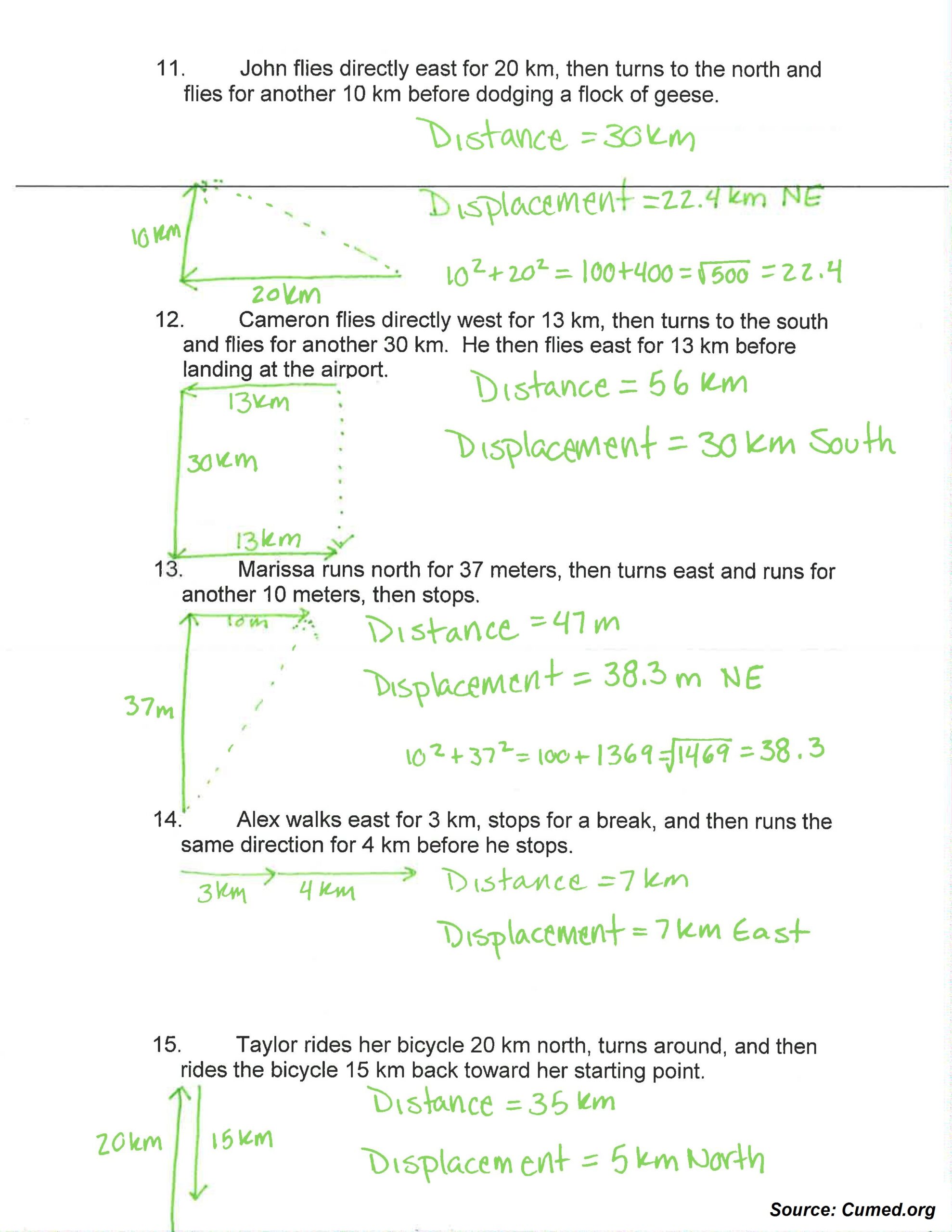

Download Distance And Displacement Worksheet
Download Distance And Displacement Worksheet: Click Here
Conceptual Distances
By analogy, the term “distance” is also used to quantify non-physical objects in particular ways.
There is a concept in computer science that describes the “edit distance” between two strings. Words like “dog” and “dot,” which only differ by one letter, are more intimate than words like “dog” and “cat,” which differ by three letters. This concept is used in coding theory and spell checks and is theoretically stated in a variety of different ways, including:
- Levenshtein separation
- Hamming range
- Lee separation
- Jaro-Winkler separation
A metric space is a collection in mathematics where all set members’ distances are specified. This allows for the determination of various “distances,” including traversing graphs, contrasting patterns and curves, and using unconventional interpretations.
